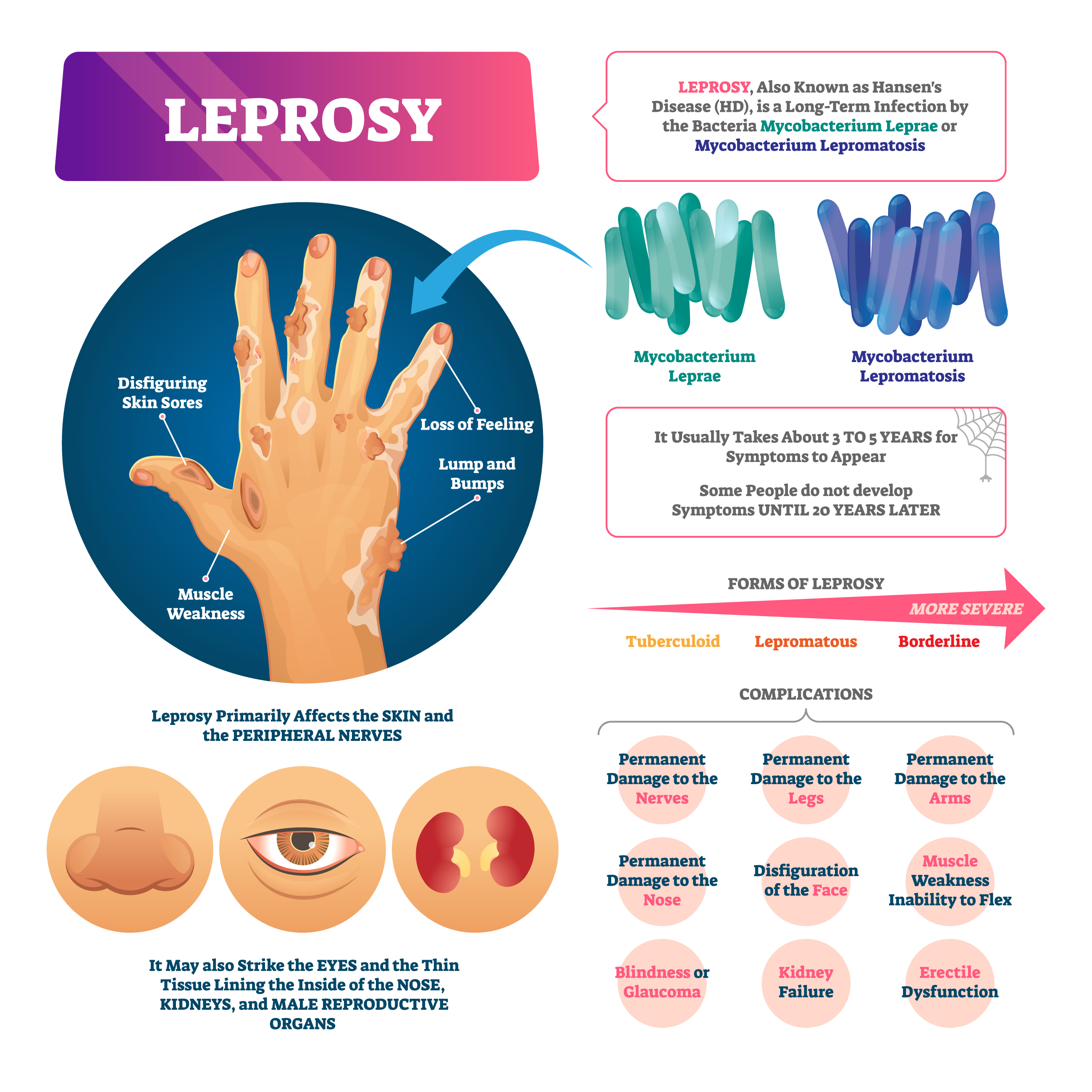
WORLD LEPROSY DAY: The infectious disease is caused by a specific type of bacteria, called Mycobacterium leprae that targets the human body’s nervous system. World Leprosy Day is observed on the last Sunday in the month of January every year. The day aims to create awareness about a disease that still has many misconceptions surrounding it.
ALSO READ: World Leprosy Day 2023: Theme, History and Significance
Leprosy, also called Hansen’s disease, is one of the oldest diseases known to mankind. The day is also observed to educate people about the condition, the plight of people suffering from it, and the treatment options available. Another major problem is the social discrimination against leprosy patients prevailing in many countries.
World Leprosy Day is an attempt to enable the people suffering from this condition to live a normal life.
On this World Leprosy Day, let’s do away with some of the most prevalent myths surrounding the disease.
Myth 1: Leprosy Is Easy To Catch
Leprosy is hard to catch. According to the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) 95 percent of adults cannot catch it. This is because an adult immune system can fight off the bacteria that cause this disease.
Myth 2: Leprosy Can Make Fingers And Toes Fall Off
Fingers and toes do not “fall off” due to leprosy. The bacteria that causes leprosy, Mycobacterium leprae, attacks the nerves of fingers and toes, according to CDC. This causes them to become numb. When that happens, burns and cuts may go unnoticed. This is the primary cause behind infection and permanent damage. However, this happens in advanced stages of untreated leprosy.
Myth 3: Leprosy No Longer Exists
Leprosy can be traced back from 600 BC to possibly as early as 1400 BC in India, making it the oldest disease known to mankind. It is still around today. Though most developed countries do not have any cases of leprosy, the disease still exists in other countries. It is most prevalent in Asia, Africa, and South America.
Myth 4: Only Poor People Get Leprosy
People who live in poorer areas are more prone to the disease. This is because leprosy affects individuals with weak immune systems. People living in backward areas are likely to have poor sanitation and nutrition, which is why they are more likely to contract it. It still depends on a person’s predisposition and their immune system. This means people who are wealthy are as much at risk of having leprosy compared to the poor.
Myth 5: Leprosy is incurable
Leprosy has a cure. The disease can be treated with multi-drug therapy, or MDT. After receiving this multi-drug therapy for 72 hours, it prevents the disease from spreading and the leprosy does not remain infectious.
Myth 6: You Shouldn’t Touch Anyone With Leprosy
The disease is only mildly infectious, with 95 percent of the world’s population already immune to it. It is not easily transmitted which means those who have leprosy are not “untouchable”. Multi-Drug Therapy (MDT) is a highly effective treatment. It only takes 72 hours for the drug to work and anyone with leprosy won’t be infectious.
Read all the Latest Lifestyle News here